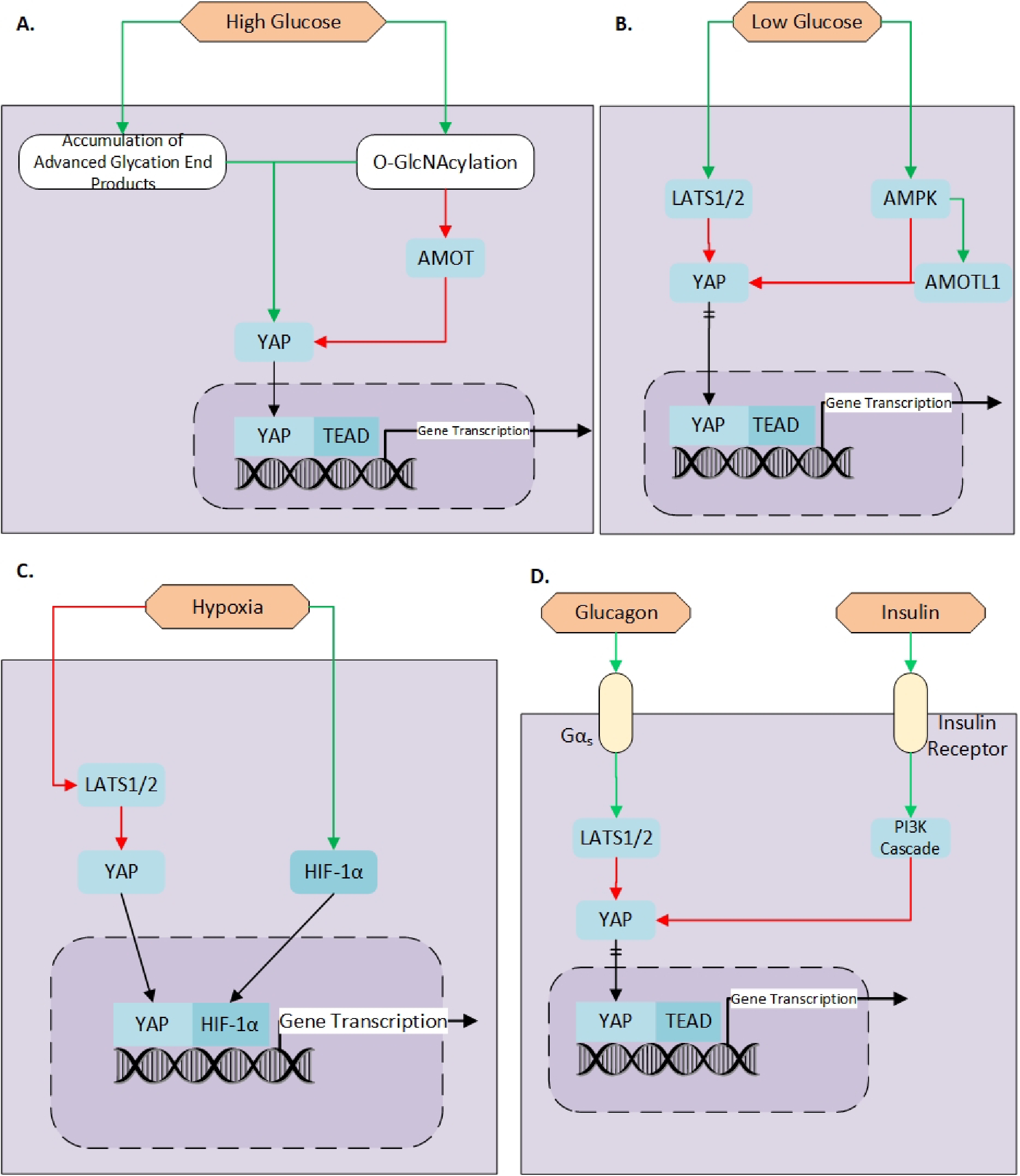
Fig. 3. The regulation of YAP concerning metabolic cues. A: High glucose condition induced the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGE) and O-GlcNAcylation through the enzyme O-GlcNAc transferase (enzyme not showed). Both AGE and O-GlcNAcylation increased the amount of unphosphorylated YAP. A detailed explanation of the mechanism is provided in the accompanying text. Additionally, the O-GlcNAcylation of AMOT also decreased AMOT's ability to bind YAP and sequester in the cytoplasm, thereby increasing the amount of nuclear YAP. B: Low glucose condition induced the activation of LATS1/2 and AMPK. Both kinases phosphorylated YAP and inhibited YAP's translocation to the nuclear compartment. Therefore, high glucose conditions increased the activity of YAP, and low glucose conditions inhibited it. C: The effects of hypoxia were shown to be partially mediated by YAP in addition to HIF-1α. Hypoxia inhibited the LATS1/2 function, which releases the control of the Hippo pathway on YAP. Therefore, allowing YAP to translocate to the nucleus to exert its transcriptional activity. Additionally, YAP was shown to bind HIF-1α and induce its stabilization and increase its half-life. YAP and HIF-1α formed a complex inside the nuclear compartment where it exerted its gene transcriptional activity. D: The effects of glucagon and insulin on YAP is shown. Glucagon induced LATS1/2 activation through binding with the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) Gαs. Activation of LATS, in turn, increased YAP phosphorylation and inhibited its nuclear translocation. Insulin bind with the insulin receptor and, through the activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, phosphorylated YAP. Green arrows denote positive effects. Red arrows denote negative or inhibiting effects. Black arrows denote the translocation of protein between compartments. Black arrows with two dash denote inhibition of translocation. Light purple boxes with a solid black line represent the cellular compartment. Dark purple boxes with dashed lines represent the nuclear compartment. AMOT: angiomotin, AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase, HIF-1α: Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Alpha, LATS1/2: Large tumor suppressor kinase 1/2, TEAD: TEA Domain Transcription Factor, YAP: Yes-associated protein.